Opengl Library
There are several types of Open Graphics Library® (OpenGL®) libraries that can be installed and used on computer systems, and most of them serve specific needs of graphics programmers. The first type includes the basic, core OpenGL® libraries, which contain roughly 120 commands to allow access to graphics hardware, although these OpenGL® libraries can be further divided depending on the platform on which they are intended to operate. Many utility libraries have been created — some of which are almost always used by OpenGL® programmers — to help group very-low-level functions into single higher-level calls for convenience and code clarity. There occasionally are OpenGL® libraries that are developed by the specific manufacturers of graphics hardware to help boost performance or support special effects that the hardware performs natively. There also are very-high-level user-created libraries that have spawned from larger projects and are distributed to assist in rapid application development.

OpenGL Mathematics (GLM) is a C mathematics library for 3D software based on the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) specification. Libktx, part of the KTX tool set, is a library of functions for writing KTX format files and instantiating GL textures from them. OpenSceneGraph is a high-level 3D graphics toolkit exposing OpenGL's capabilities while. Jun 25, 2021 The GL3W library focuses on the core profile of OpenGL 3 and 4. It only loads the core entrypoints for these OpenGL versions. It only loads the core entrypoints for these OpenGL versions. It supports Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and FreeBSD. An OpenGL library GLFW. GLFW is an Open Source, multi-platform library for OpenGL, OpenGL ES and Vulkan development on the desktop. It provides a simple API for creating windows, contexts and surfaces, receiving input and events. GLFW is written in C and supports Windows, macOS, X11 and Wayland. GLFW is licensed under the zlib/libpng license. MathFu - C math library developed primarily for games focused on simplicity and efficiency. Newton - It is a cross-platform life-like physics. OGLplus - Collection of libraries which implement an object-oriented facade over OpenGL. SDL - Designed to provide low level access to multimedia and graphics hardware.
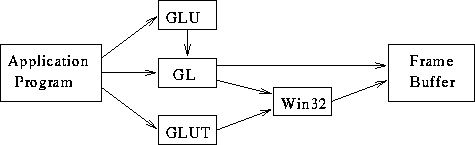
Core OpenGL® libraries are necessary for the development and deployment of programs that use OpenGL® to render graphics. They allow programs to use a common abstract programming interface (API) to call the functions inside the OpenGL® library, after which the library will interact directly with hardware drivers. The drivers then access the hardware directly, causing an increase in display speed. All other OpenGL® libraries are based on the core libraries.
Opengl Library Windows 10

Many of the commands used by the core libraries are fairly low level, so a number of utility libraries, also called toolkits, have been created. These bundle the basic commands into more functional routines that take much of the repetition out of using OpenGL®. One example of using a utility library involves drawing a circle, which could take several lines of code with just core OpenGL® but can be condensed into one optimized routine within a utility library such as the OpenGL® Utility Toolkit (GLUT). Occasionally, some libraries share the same name but are ported for use on different operating systems or for different language bindings, and they might contain different functionalities.
Some OpenGL® libraries are actually produced by hardware manufacturers. Extended libraries can be access though the OpenGL® extensions mechanism or directly with APIs provided by the manufacturers. These types of libraries do not always see widespread use because of their narrow target platforms and because very popular extensions are often folded into the core libraries.
There also are OpenGL® libraries that are created by programmers and users that are not associated with the core libraries or any hardware. These libraries are often released so other programmers who are creating certain types of scientific, mathematical or entertainment applications can benefit from having a framework on which to build. There also are community-derived libraries that add interactivity and program logic to the other libraries in a practical way.
There are numerous Windowing system and interface libraries available for OpenGL as well as Scengraphs and High-level libraries build on top of OpenGL
Java Opengl Library
- About GLUT
- GLUT is the OpenGL Utility Toolkit, a window system independent toolkit for writing OpenGL programs. It implements a simple windowing application programming interface (API) for OpenGL. GLUT makes it considerably easier to learn about and explore OpenGL Programming.
- Other GLUT-like Window System Toolkits
- Libraries that are modeled on the functionality of GLUT providing support for things like: windowing and events, user input, menuing, full screen rendering, performance timing
- About GLX, GLU & DRI
- GLX is used on Unix OpenGL implementation to manage interaction with the X Window System and to encode OpenGL onto the X protocol stream for remote rendering. GLU is the OpenGL Utility Library. This is a set of functions to create texture mipmaps from a base image, map coordinates between screen and object space, and draw quadric surfaces and NURBS. DRI is the Direct Rendering Infrastructure for coordinating the Linux kernel, X window system, 3D graphics hardware and an OpenGL-based rendering engine.
GLX, GLU and DRI
GLXLibrary
GLX 1.3 is used on Unix OpenGL implementation to manage interaction with the X Window System and to encode OpenGL onto the X protocol stream for remote rendering. It supports: pixel buffers for hardware accelerated offscreen rendering; read-only drawables for preprocessing of data in an offscreen window and direct video input; and FBConfigs, a more powerful and flexible interface for selecting frame buffer configurations underlying an OpenGL rendering window.
- Please refer to the OpenGL Registry for more information and links
GLU Library
GLU is the OpenGL Utility Library. This is a set of functions to create texture mipmaps from a base image, map coordinates between screen and object space, and draw quadric surfaces and NURBS. GLU 1.2 is the version of GLU that goes with OpenGL 1.1.
GLU 1.3 is available and includes new capabilities corresponding to new OpenGL 1.2 features.- Please refer to the OpenGL Registry for more information and links
Direct Rendering Infrastructure (DRI)
In simple terms, the DRI enables hardware-accelerated 3D graphics on Linux. More specifically, it's a software architecture for coordinating the Linux kernel, X window system, 3D graphics hardware and an OpenGL-based rendering engine.
- Higher Level Libraries built on OpenGL
- Leading software developers use OpenGL, with its robust rendering libraries, as the 2D/3D graphics foundation for higher-level APIs. Developers leverage the capabilities of OpenGL to deliver highly differentiated, yet widely supported vertical market solutions. Open Inventor, IRIS Performer, OpenGL Optimizer, OpenGL Volumizer, OpenGL Shader, Scene Graph APIs.
- Open Inventor® by VSG
- Open Inventor® by VSG is the commercial, current evolution of Open Inventor and provides an up-to-date, highly-optimized, full-featured implementation of the popular object-oriented scenegraph API for C++, .NET and Java. Applications powered by Open Inventor by VSG also benefit from powerful extensions such as VolumeViz LDM for very large volume data, MeshViz XLM for high-performance mesh support, or ScaleViz for multi-GPUs and immersive VR.
- OpenSceneGraph
- OSG is a open source high peformance 3D graphics toolkit, used by application developers in fields such as visual simulation, games, virtual reality, scientific visualization and modelling. Written entirely in Standard C++ and OpenGL it runs on all Windows platforms, OSX, Linux, IRIX, Solaris and FreeBSD operating systems.
- Quesa3D
- Quesa is a high level 3D graphics library, released as Open Source under the LGPL, which implements Apple's QuickDraw 3D API on top of OpenGL. It supports both retained and immediate mode rendering, an extensible file format, plug-in renderers, a wide range of high level geometries, hierarchical models, and a consistent and object-orientated API. Quesa currently supports Mac OS, Linux, and Windows - ports to Be and Mac OS X are in progress.